
 | |
Строительный блокнот Introduction to electronics 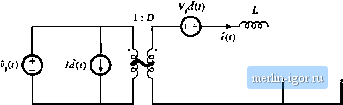 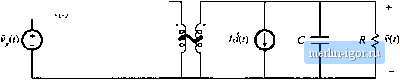 1 : D   Fig. 7.17 Averaged small-signal ac models for several basic converters operating in continuous conduction mode: (a) buck, (b) boost, (c) buck-boost. 1 : л
Fig. 7.18 Flybackconverterexarnple. 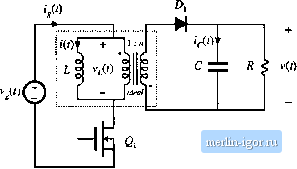 Transformer model 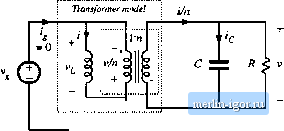 Fig. 7.19 Flyback convener example: (a) incorpnration of trans farmer equivalent circuil, (b) circuit during sub-interval 1, (c) circuit during suliiutcrval 2. reduces to Fig. 7.19(b). The inductor voltage l(f), capacitor current ((-(t), and converter input current ! (0 ;u-e: v(rt = v,(f)-i(f)ff /c(0= /f> = (f) (7.51) We next inake the small ripple approximation, replacing the voltages and currents with their average val- ues as defined by Eq. (7.3), to obtain (ко),; (7.52) Duriag the second subinterval, MOSFET Qi is off, ditxle Dj conducts, and the circuit of Fig. 7.19(c) is obtained. Analysis of this circuit shows that the inductor voltage, capacitor current, and input current are given by (0 = -t> ,(0 = 0 (7,53) The small-ripple approximation leads to Vi.il) =--й- cW--n--- (7.54) The inditctor voltage and current waveftirms are slietched in Fig. 7.20. The average inductor voltage can now be found by averaging the waveform of Fig. 7.20(a) over one switching period. The result is
(b) CO  0 dT 7; t Fig. 7.20 Inductor wavefurtns for the flyback example; (a) inductor voltage, (h) inductor current. |